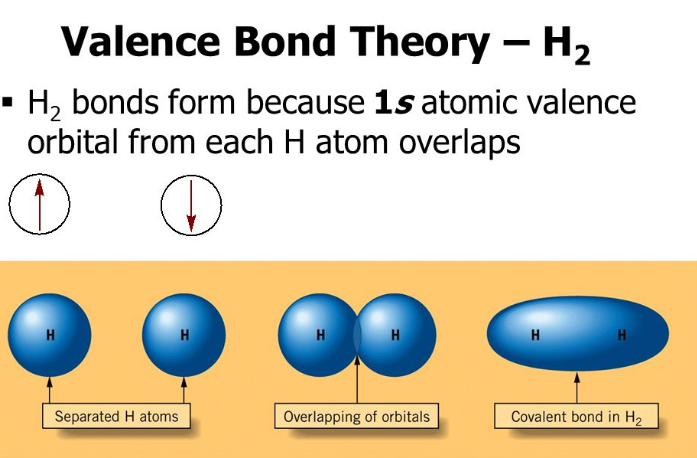
Valence bond theory describes bonding as a consequence of the overlap of two separate atomic orbitals on different atoms that creates a region with one pair of electrons shared between the two atoms. The s orbitals are filled and do not overlap.
10 Difference Between Valence Bond Theory Vbt And Molecular Orbital Theory Mot With Examples Viva Differences
Valence bond theory describes bonding as a consequence of the overlap of two separate atomic orbitals on different atoms that creates a region with one pair of electrons shared between the two atoms.
. O half filled orbitals hybrid orbitals completely filled orbitals Consider the following image. Use valence bond theory to explain the bonding in O2. Key Concepts and Summary.
Textbook solution for General Chemistry - Standalone book MindTap Course 11th Edition Steven D. For many years after they were discovered it was believed that the noble gases could not form compounds. The valence bond theory explains the formation of covalent bonds.
Valence bond theory was used to explain the structure of coordination compounds and the bond linkages. Sketch the overlap of the atomic orbitals involved in the bonds in O2. It also helps in finding the electronic structure of molecules.
O The greater the overlap between the orbitals on two atoms the stronger the bond. Gammon Chapter 21 Problem 21121QP. We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts.
Valence bond theory describes a chemical bond as the overlap of atomic orbitals. When the orbitals overlap along an axis containing the nuclei they form a σ bond. Key Concepts and Summary.
C Determine the hybridization of each type of carbon atom. Valence bond theory explains the overlapping of atomic orbitals. B Lone pair electrons are in atomic orbitals or in hybrid atomic orbitals.
It is one of two prominent theories that help to explain how atoms join together. Which of the following is not a valence bond concept. According to valence bond theory the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its n-1d ns np nd orbitals.
O A pair of electrons in a bond is shared by both atoms. Valence bond theory describes the electronic structure of molecules. Which of the following is not a valence bond concept.
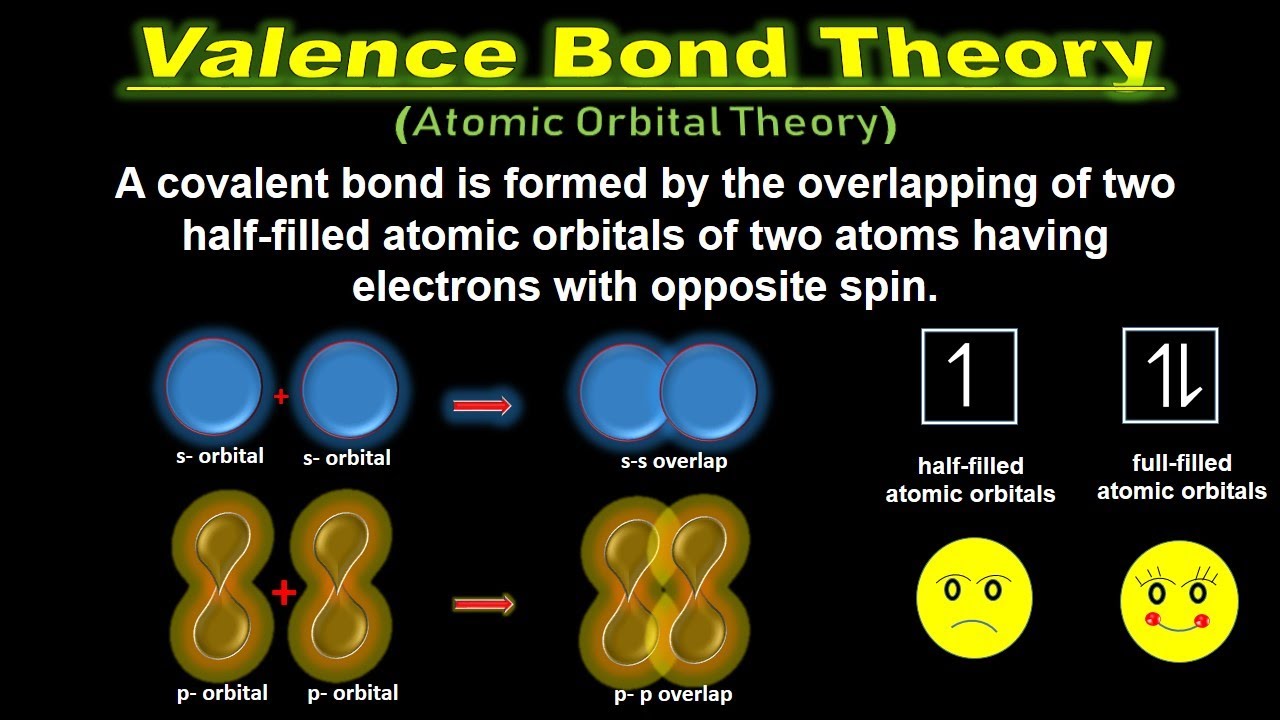
Covalent bonds are formed when two valence orbitals half-filled belonging to two different atoms overlap on each other. Lone pair electrons are in atomic orbitals or in hybrid atomic orbitals. When the orbitals overlap along an axis containing the nuclei they form a σ bond.
The electron density in the area between the two bonding atoms increases as a result of this overlapping thereby increasing the stability of the. Which of the following is not a valence bond concept. 71 Which of the following is not a valence bond concept.
A True b False Answer. The valence bond theory explains the structure and magnetic properties of a large number of coordination compounds. O Lone pair electrons are in atomic orbitals or in hybrid atomic orbitals.
Now we know that belief to be incorrect. Which of the following is not a valence bond concept. The greater the overlap between the orbitals on two atoms the stronger the bond.
One σ bond and one π bond. When the orbitals overlap along an axis containing the nuclei they form a σ bond. This concept proposes that since the attached groups are not at the angles of the p orbitals and their atomic orbitals would not have maximum overlap to form strong bonds the s and p.
A each of the bonded atoms maintains its own atomic orbitals B Lone pair electrons are not in atomic orbitals or in hybrid atomic orbitals. It states that the covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of valence shell atomic orbitals of the two atoms having unpaired electrons. MCQs on Valence Bond Theory.
D A pair of electrons in a bond is shared by both atoms. A each of the bonded atoms maintains its own atomic orbitals B Lone pair electrons are not in atomic orbitals or in hybrid atomic orbitals Get the answer to your homework problem. Valence bond theory was initially introduced by London and Heitler and was developed by Pauling and others.
Now we move on and look at the various postulates of the valence bond theory. Atomic orbitals on two atoms may overlap to form antibonding orbitals. It is based on quantum mechanics.
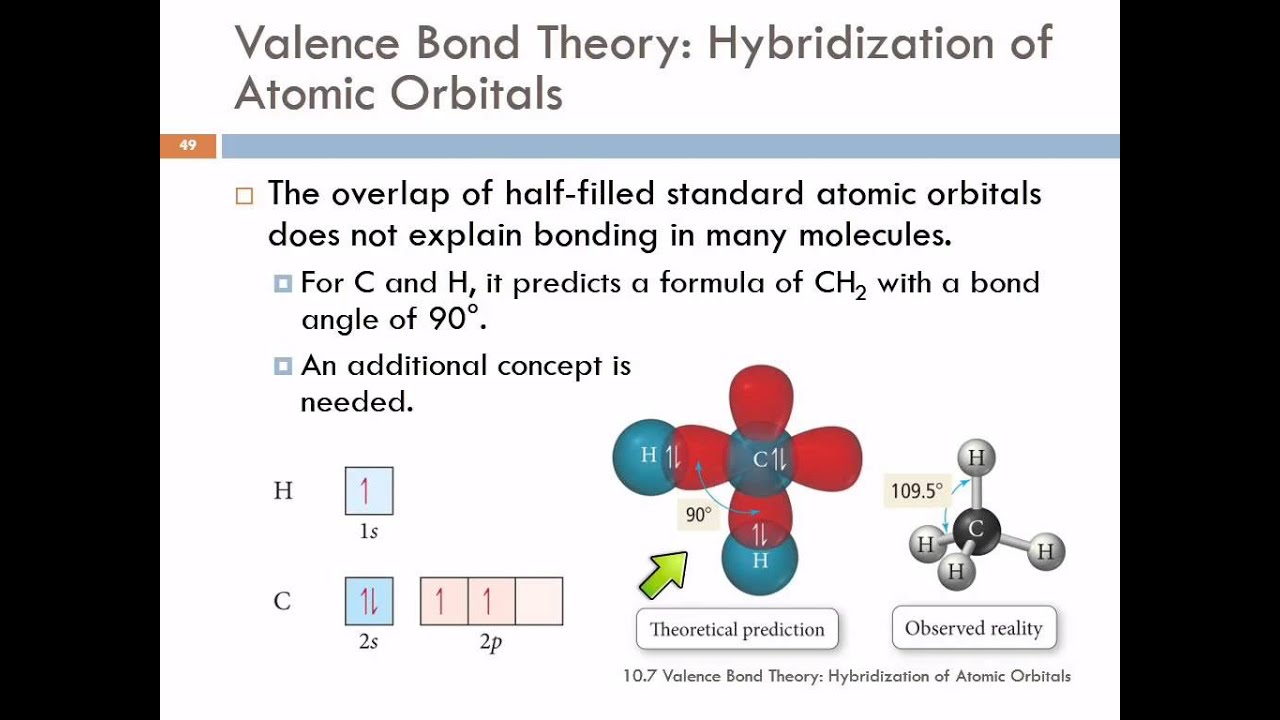
The important postulates of the valence bond theory are listed below. The valence bond theory was proposed by Heitler and London to explain the formation of covalent bond quantitatively using quantum mechanics. B Predict the geometry about the carbon atom.
This problem has been solved. For each of the four carbon compounds do the following. To explain chemical bonding the Valence Bond Theory VBT looks at the interaction between atoms.
A The greater the overlap between the orbitals on two atoms the stronger the bond. The main postulates of this theory are as follows. The extent of overlap is a deciding factor of the covalent bond strength.
O Atomic orbitals on two atoms may overlap to form anti bonding orbitals. Valence Bond Theory was proposed by Heitler and London. Rather than a linear molecule with the hydrogen atoms at a 180o bond angle.
Later on Linus Pauling improved this theory by introducing the concept of hybridization. A covalent bond is formed by the overlapping of two half. Key Concepts and Summary.
Sp3-sp3 overlap O s-p overlap sp3-s overlap Which of the following. A pair of electrons in a bond is shared by both atoms. A Draw a Lewis structure.
C Atomic orbitals on two atoms may overlap to form antibonding orbitals. The p orbitals overlap along the axis to form a σ bond and side-by-side to form the π bond. The theory says that electrons fill the atomic orbitals of an atom within a molecule.
Which orbital overlap is not pictured here. Its a chemical bonding theory that explains the overlapping the atomic orbitals in order to form chemical bonds between atoms. Valence bond theory describes bonding as a consequence of the overlap of two separate atomic orbitals on different atoms that creates a region with one pair of electrons shared between the two atoms.
It also states that the nucleus of one atom is attracted to the electrons of another atom. According to the valence bond theory the which is not a requirement for the formation of a covalent bond.
Valence Bond Theory Class 11 Chemistry Vbt Chemical Bonding 02 11th Class Chemistry Chapter 3 Youtube

10 6 10 7 Valence Bond Theory Orbital Overlap Hybridization Of Atomic Orbitals Youtube

Valence Bond Theory Need Postulates Limitations Examples And Videos

0 Comments